Alphabet Inc. (Google): AI Leadership and Regulatory Risks
How Alphabet is adapting to AI competition and regulatory scrutiny while leveraging its strengths to sustain dominance
In a previous article, I analyzed Alphabet’s fundamentals, including its dominance in Search, YouTube’s growth, Google Cloud’s expansion, and Waymo’s long-term potential. For a deeper analysis of Alphabet’s business, my investment thesis, and its place in my portfolio, I encourage you to read the first article of this multi-part series.
Building on that foundation, this article focuses on Alphabet’s opportunities and challenges in the AI era and regulatory risks.
AI Revolution: Challenge or Opportunity for Alphabet?
Alphabet has long been at the forefront of artificial intelligence (AI) innovation, enhancing its core businesses while expanding into new markets. Yet, as the AI revolution accelerates, competition is intensifying.
The rise of generative AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT has reshaped how users interact with information, offering conversational responses that challenge traditional keyword-based search models. Some market commentators and analysts speculate that generative AI could erode Alphabet’s core Search business, which accounts for the lion’s share of ad revenue and profit.
I disagree.
This perspective oversimplifies the AI landscape by equating artificial intelligence solely with large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. While LLMs represent a breakthrough, their long-term differentiation is likely to diminish as the technology becomes commoditized: The performance gap between the best and second-best models will narrow over time, driven by advances in compute power and talent, resources that Alphabet already possesses in abundance.
Instead of focusing narrowly on standalone LLMs, it’s critical to recognize that AI’s real impact lies in its integration into tools and platforms that users already rely on daily. This is where Alphabet holds a structural advantage and wide economic moat1. Google’s AI capabilities are deeply embedded across its ecosystem: Search, Workspace, Maps, YouTube, and Cloud, leveraging massive network effects that protect it from competition, even in a world of commoditized AI models. Operating a three-sided ecosystem that connects users, advertisers and content creators, Google benefits from significant exit barriers: Businesses and creators depend on Google for monetization through AdSense, visibility via Search, and advertising through Google Ads, making the cost of switching prohibitively high. For users, incentives to leave are equally limited.
While AI chatbots deliver quick answers, they lack the interactive and exploratory experience users value. Searching multiple sources, evaluating information, and comparing perspectives offers intellectual satisfaction and confidence in decision-making. Researching products or planning trips, for instance, is as much about the process as the outcome. By contrast, AI-generated answers can feel static and impersonal, diminishing the satisfaction derived from discovery.
That said, younger users accustomed to instant gratification and bite-sized content on TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat may prioritize speed and convenience over depth and deliberation. AI chatbots cater to this preference, offering ready-made answers rather than requiring extensive research. This dichotomy challenges the idea that the search process itself holds intrinsic value for all users.
Google’s ability to adapt to these shifting habits strengthens its competitive edge. Features like AI Overviews in Search and YouTube Shorts cater to younger audiences while maintaining the depth and credibility valued by older users. Meanwhile, Gemini’s integration into Search, Workspace, and Maps delivers dynamic, context-aware responses that bridge the gap between exploration and direct answers. This hybrid approach allows Alphabet to appeal to both generations, reinforcing its role as a platform for all users.
Despite fears of disruption, Alphabet’s performance remains strong. Advertising revenue and profit continue to grow at a mid-to-high teens rate year-over-year, even as competition intensifies. The company retains nearly 90% of the search market share, with users averaging 200 searches per month, an increase from the previous year.
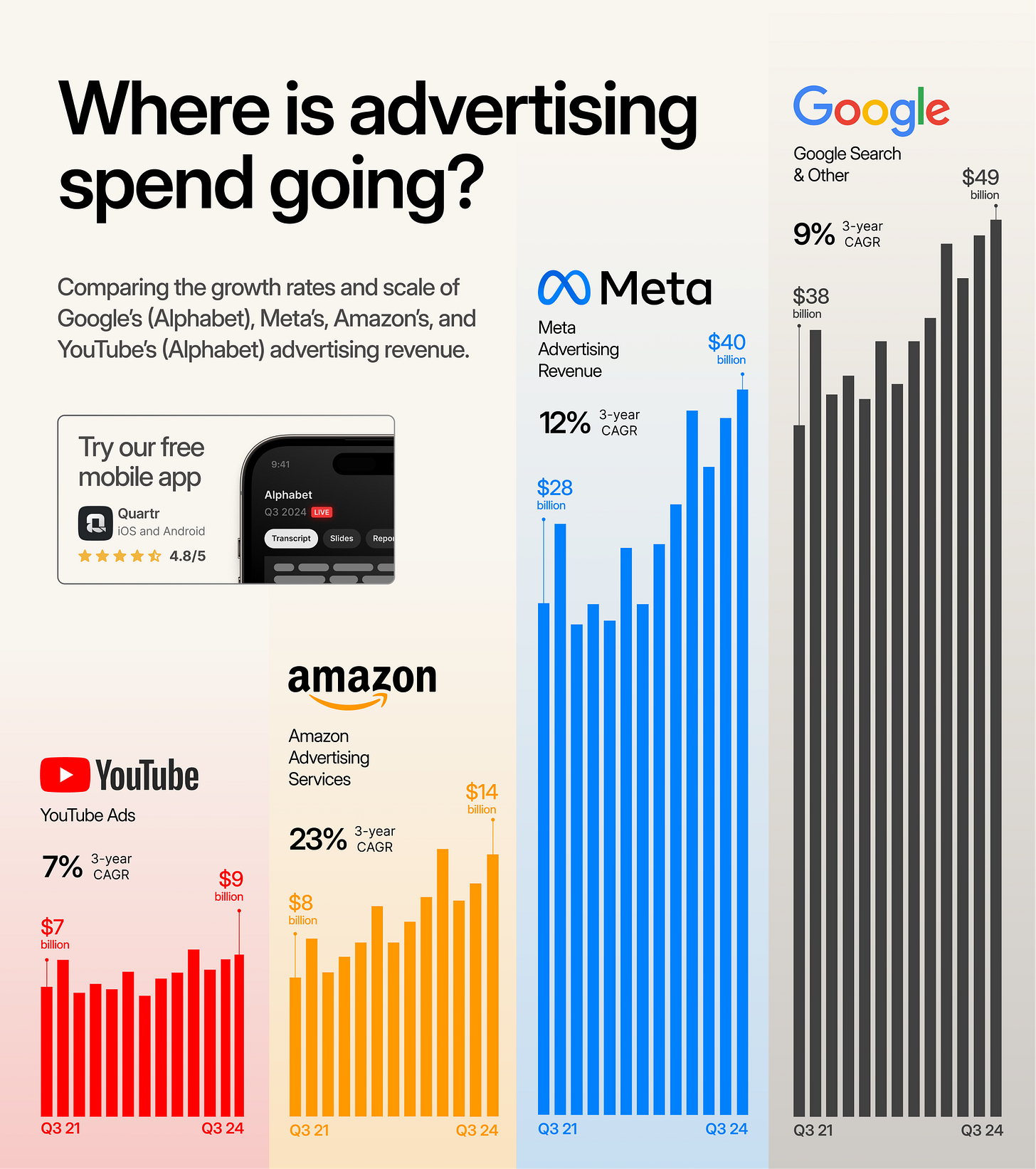
While competition in generative AI is inevitable, Alphabet’s technical infrastructure, scale, and ability to embed AI across its products provide durable advantages. Rather than a threat, AI represents an opportunity to make Alphabet’s ecosystem smarter, faster, and more relevant, reinforcing its dominance in the years ahead.
How Google’s Foundations Shaped ChatGPT’s Rise
In November 2022 the launch of ChatGPT sent shockwaves through the tech industry and captured global attention, showcasing the transformative potential of AI. Developed by OpenAI, ChatGPT is an advanced AI large language model (LLM) that leverages natural language processing (NLP) to generate human-like text responses, assists with tasks such as content creation, coding, brainstorming, and simulates conversations.
ChatGPT is built on the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) architecture, which itself is based on the Transformer model. This revolutionary framework was first introduced by researchers at Google Brain, in their groundbreaking 2017 paper, Attention is All You Need, authored by Ashish Vaswani and his team.
Alphabet’s pioneering role in developing the Transformer model underscores the company’s long-standing commitment to AI research and its role in shaping the field of artificial intelligence. OpenAI later adapted and enhanced this foundation, optimizing it for unsupervised language pre-training and text generation tasks, which ultimately led to the creation of GPT and ChatGPT.
Ever since the launch of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, there has been a proliferation of well-funded AI-powered chatbots like xAI’s Grok and Anthropic’s Claude, and conversational search engines such as Perplexity AI. Some companies, rather than developing their own AI capabilities, have opted to partner with established AI models, notably the Apple-OpenAI partnership.
At Alphabet, the development of Google Bard and its evolution into Google Gemini highlights Alphabet’s rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and its strategic response to growing competition in the AI landscape.
Gemini’s Ascent: Alphabet’s Vision for AI at Scale
In February 2023, Google launched Bard, an AI-powered chatbot built on Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA) to rival ChatGPT. Initially available in the U.S. and U.K., Bard expanded globally by May 2023, supporting over 40 languages and integrating tools like Google Lens and coding platforms. Its foundation shifted to Pathways Language Model 2 (PaLM), enabling multimodal capabilities for text, images, and code generation. However, Bard’s rushed rollout was marred by technical glitches and high-profile errors, including an inaccurate response in its public demo. Market commentators and some news outlets questioned Google’s preparedness, and the incident exposed the challenges of deploying AI tools at scale. Alphabet responded quickly by accelerating improvements, refining Bard’s accuracy, and incorporating feedback, setting the stage for its rebranding into Gemini.
By early February 2024, Bard was rebranded as Gemini, powered by a multimodal AI model capable of handling text, images, audio, video, and code. With the release of Gemini 1.0, Google positioned itself as a direct competitor to OpenAI’s GPT-4. The launch of Gemini 1.5 in mid-February 2024 improved scalability, efficiency, and long-context processing, leveraging a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture to handle larger datasets while reducing computational costs. Gemini 1.5 also introduced in-context learning, allowing it to acquire new skills without retraining.
In May 2024, Google introduced Gemini Nano, a lightweight version optimized for on-device AI in Google Pixel devices, enabling offline functionality and enhancing privacy without compromising performance.
By mid-2024, Gemini had allegedly surpassed 70 million users, becoming a foundational AI layer deeply integrated across Search, Workspace, and Cloud. This rapid adoption underscores Alphabet’s dual focus on consumer applications and enterprise AI solutions, demonstrating its ability to scale AI globally while driving innovation throughout its ecosystem.
Gemini 2.0, launched on December 11, 2024, represents a major leap in AI technology. With enhanced multimodal capabilities, faster performance, and real-time interaction, Gemini 2.0 redefines AI’s role in Alphabet’s ecosystem. Seamlessly embedded into Search, Lens, and Maps, Gemini 2.0 delivers context-aware assistance, enabling users to tackle complex tasks and elevate their experiences.
One of the defining features of Gemini 2.0 is its agentic AI capabilities, enabling the model to autonomously execute tasks with minimal human input. From scheduling appointments and online shopping to analyzing data and planning workflows, Gemini’s ability to make independent decisions represents a transformative shift toward AI autonomy. Backed by Trillium Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), Gemini 2.0 offers 4.7x more compute power than its predecessors, enabling low latency, high scalability, and cost-efficient performance.
As Gemini continues to evolve, Alphabet’s vision extends beyond current capabilities. With Gemini 2.0 serving as a stepping stone toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), Alphabet is laying the foundation for autonomous systems, personal AI assistants, and AI-driven ecosystems that will reshape how we work, create, and live.
Alphabet’s ability to scale AI responsibly, combined with its deep technical expertise and infrastructure advantages, ensures it remains at the forefront of the AI revolution, turning challenges into opportunities and cementing its role as a global AI leader.
AI Leadership and Monetization through AI
In May 2024, Alphabet’s AI strategy took center stage during Google’s I/O developer conference, where the company announced the rollout of AI Overviews for its core Search product, which provides AI-generated summary responses.
Preliminary results from the past six months suggest that AI Overviews are delivering richer, more context-aware search results, effectively addressing complex queries while improving efficiency. Users engaging with AI-generated responses are searching more frequently, spending more time on linked websites, and submitting more detailed queries, signaling higher engagement and richer search intent. These trends counter skepticism that AI might undermine Google’s advertising model. Instead, Alphabet has shown that AI integration not only enhances user experience but also boosts ad performance through improved targeting and higher click-through rates2.
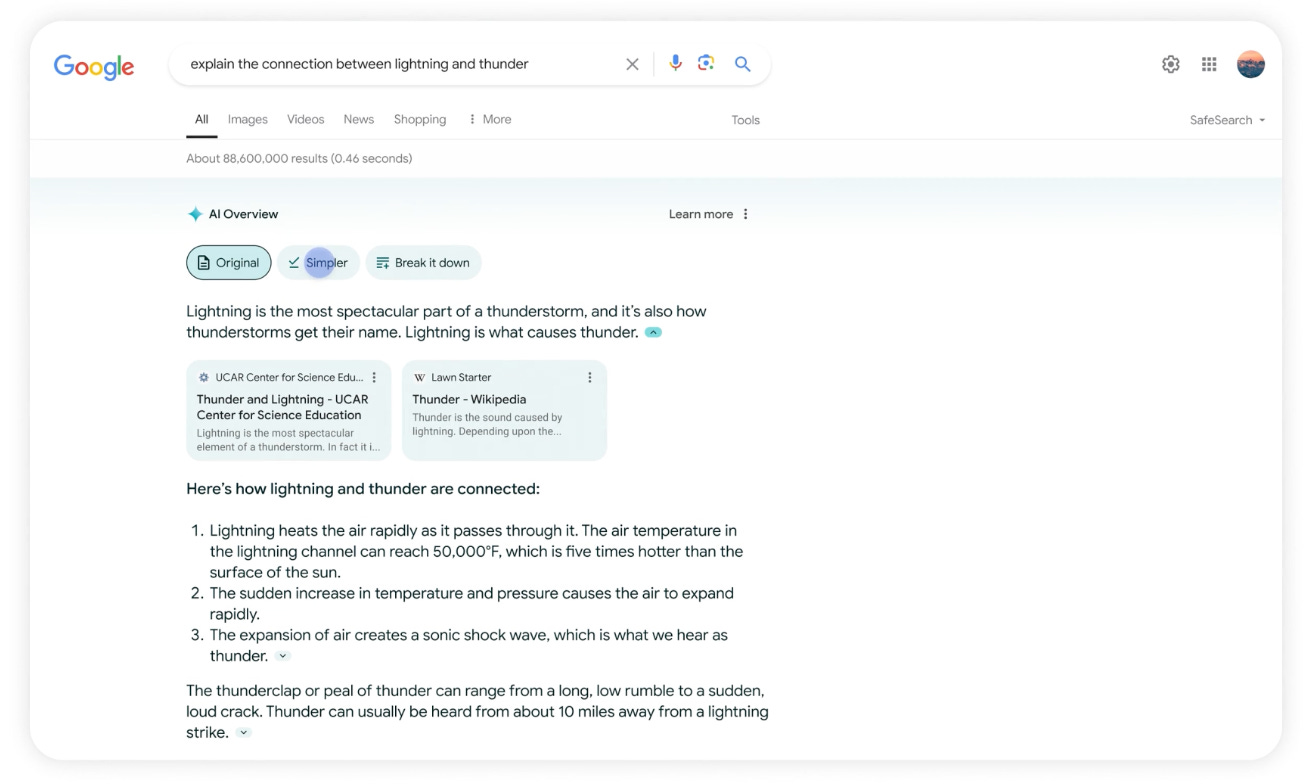
Alphabet is already testing ad placements within AI Overviews, which are delivering comparable monetization rates to traditional search ads. Over time, the richer, context-aware responses provided by AI Overviews could improve ad targeting and conversion rates, unlocking new monetization potential.
Despite the rising competition, Alphabet’s moat remains formidable, and its position in AI is reinforced by several key advantages:
Technical infrastructure: Years of investment in AI research and optimization, including custom hardware (TPUs) and advanced algorithms, enable Alphabet to scale AI platforms efficiently and cost-effectively.
Global reach: Alphabet’s platforms collectively serve over 2 billion users, providing an unparalleled audience base that competitors struggle to match.
Brand trust and habit: The ingrained habit of Googling has made Alphabet synonymous with search, fostering trust and user loyalty that allow it to weather occasional missteps while retaining dominance.
Alphabet’s technical infrastructure, global reach, and brand trust create barriers competitors struggle to match: With 2 billion active users, the entrenched habit of Googling, and homegrown Trillium TPUs, Alphabet retains an economic competitive advantage and a technical edge that newer entrants like OpenAI, xAI, and Anthropic cannot easily replicate.
Scaling AI Products
Alphabet’s ability to deploy AI at scale further strengthens its moat. With AI Overviews currently reaching 1 billion users in over 100 countries, this rollout highlights Google’s proprietary infrastructure, optimized for AI and machine learning applications for over a decade. Notably, the compute costs per AI query have fallen by over 90% in the past 18 months, demonstrating Alphabet’s efficiency in scaling AI without compromising profitability.
AI Expansion Beyond Search
Google Cloud has rapidly emerged as a robust platform for enterprise AI adoption and innovation. Its growth is driven by AI-optimized infrastructure, enabling businesses to develop applications, streamline workflows, and integrate AI solutions seamlessly. With over 70% of generative AI startups building on Google Cloud, the platform has solidified its competitive position as the go-to choice for AI development and deployment.
Alphabet’s continued investment in TPUs and its Vertex AI platform has enhanced scalability and efficiency, allowing enterprises to process vast datasets and train complex models at lower costs. These advancements have positioned Google Cloud as a compelling alternative to Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, especially as it narrows the profitability gap with AWS’s 35% operating margins. With margins improving and revenue growth accelerating, Google Cloud is poised to become a major earnings contributor for Alphabet, fueled by AI-driven innovation and enterprise adoption.
AI’s integration into Google Workspace has further strengthened Alphabet’s position in enterprise productivity tools, directly competing with Microsoft’s O365 Copilot. Unveiled in May 2023 as Duet AI and later rebranded to Gemini, this AI-powered suite offers features like email drafting, document summarization, advanced spreadsheet analysis, and real-time meeting transcription. These features not only enhance productivity but also reduce repetitive tasks, enabling businesses to operate more efficiently. The rebranding was part of a larger strategy at Google to consolidate its AI capabilities under the Gemini umbrella, creating a unified identity for its advanced AI tools and reinforcing its commitment to seamless integration and innovation across its ecosystem.
While Microsoft’s Copilot leverages its dominance in enterprise software, Google’s approach combines affordability and seamless integration with Google Cloud and AI-powered features, making Workspace particularly appealing to startups, small businesses, and organizations prioritizing collaboration and accessibility.
Beyond cloud services and enterprise productivity, Alphabet is leveraging AI to disrupt other industries, particularly autonomous transportation. Waymo, Alphabet’s autonomous driving subsidiary, has demonstrated significant scalability, completing 150,000 weekly paid rides. Its expansion into additional major U.S. cities highlights growing consumer trust and adoption, positioning Waymo as a long-term growth driver in the autonomous mobility sector.
These advancements reinforce Alphabet’s broader AI ecosystem, combining infrastructure, enterprise solutions, and real-world applications to sustain growth and competitive leadership.
AI’s Role in Cost Efficiencies and Margin Expansion
Beyond fueling revenue growth, AI is transforming Alphabet’s operational efficiency and profitability. Over 25% of new code at Google is now written by AI, later reviewed by professional developers, accelerating software development and reducing engineering costs. AI has also optimized Google’s data centers, leveraging machine learning to reduce energy consumption for cooling by up to 40%, lowering operating expenses while enhancing sustainability. Additionally, AI-driven automation tools streamline tasks like customer support and content moderation, cutting labor costs and improving scalability. On platforms like YouTube, AI-powered content recommendations boost engagement and ad performance, increasing monetization without proportional increases in operating costs.
These efficiencies have translated into meaningful margin expansion: Alphabet’s consolidated operating margins improved by nearly 5% over the past year, reflecting disciplined cost management and the scaling of AI-driven processes. Google Cloud, which had operated at breakeven just two years ago, achieved a 17.2% operating margin, driven by rapid revenue growth, economies of scale, and AI-optimized infrastructure.
This combination of AI-powered efficiency, expanding margins, and diversified revenue growth highlights Alphabet’s ability to leverage artificial intelligence not just as a tool for innovation but as a foundational layer that enhances its entire ecosystem, driving long-term profitability and shareholder value.
The Antitrust Scrutiny: Regulatory Risks and Reality
Alphabet faces heightened regulatory scrutiny in both the U.S. and Europe, but the long-term impact may be less disruptive than headlines suggest.
A key difference between U.S. and EU antitrust laws explains much of the pressure Google faces: While U.S. regulations are primarily focused on protecting consumer welfare, EU laws aim to preserve competition itself. This difference has historically led to more aggressive enforcement and fines in Europe, such as the landmark Google Android case. EU regulators found Google guilty of abusing its dominance by bundling its search app with the Play Store, pre-installing Chrome, and offering revenue-sharing payments to manufacturers in exchange for excluding rival search engines. Although deemed anti-competitive in Europe, Google defended these practices as enhancing user experience, an argument that has traditionally held more weight under U.S. law.
However, regulatory attitudes in the U.S. are shifting. In August 2024, U.S. District Judge Amit Mehta ruled that Google maintained a search monopoly through multi-billion-dollar agreements with carriers and manufacturers, including payments to Apple to remain the default search engine on Safari.
While this ruling signals stricter enforcement, immediate disruption is unlikely. Appeals could take years, during which Google is expected to retain its dominant position. Even if the appeal fails, the most probable remedies, banning default agreements or requiring user choice, are unlikely to diminish Google’s market power. Strong brand recognition and user trust make Google the likely top choice even if users are given options, and monetization models based on paid inclusion as search options could reinforce its competitive edge.
In November 2024, the Department of Justice (DOJ) escalated its case by proposing that Google divest its Chrome browser to reduce its dominance in search. Google countered with alternative remedies, suggesting modifications to its default agreements, unbundling the Play Store from Chrome, and offering non-exclusive distribution agreements. The company argues that forced divestiture could harm innovation and user experience. A trial to determine remedies is set for April 2025. For an in-depth analysis of the situation from a professional antitrust lawyer, I recommend reading this article, The U.S. Government Wants to Break Up Google.
While these regulatory battles dominate headlines, Alphabet’s entrenched position, bolstered by network effects, technical infrastructure, and a trusted brand, makes it well-positioned to weather short-term challenges. Structural changes, if imposed, may cause operational adjustments, but they are unlikely to undermine Alphabet’s long-term dominance or growth prospects.
Conclusion
Alphabet’s story in the AI era is one of resilience, adaptability, and strategic execution. While the rise of generative AI tools like ChatGPT has fueled speculation about disruption, Alphabet has demonstrated that its strength lies in embedding AI into its existing ecosystem, enhancing products like Search, Workspace, and Cloud to meet evolving users’ needs. Its hybrid approach, combining the depth and reliability of traditional search with the speed and personalization of AI-driven capabilities, positions it to capture value across demographics, appealing to both older users seeking depth and younger users prioritizing convenience.
Beyond Search, Alphabet’s AI-powered advancements in Google Cloud and Workspace reinforce its position as a leader in enterprise solutions, while Waymo’s growth in autonomous mobility highlights its ability to apply AI in disruptive industries. Meanwhile, AI-driven efficiencies are boosting profitability, with operating margins improving and cloud services emerging as a meaningful earnings driver.
Regulatory challenges, including antitrust lawsuits and potential divestitures, remain a source of uncertainty. However, Alphabet’s entrenched market position, vast technical infrastructure, and global brand strength suggest that even significant remedies are unlikely to erode its dominance in the long term.
Ultimately, Alphabet’s ability to scale AI responsibly while driving innovation and profitability underscores its status as a global leader in artificial intelligence. As the AI landscape continues to evolve, Alphabet is well-prepared to not only defend its economic moat but also shape the future of AI applications and adoption.
In the next article of this multi-part series, I will examine Alphabet’s capital allocation strategy and assess its current valuation to determine whether the company remains an attractive investment opportunity.
For an analysis of Alphabet’s competitive advantages, including its network effects and winner-takes-all dynamics, you can refer to my previous article.
Click-through rates (CTR) refer to the percentage of users who click on a specific link after seeing it in search engine results pages (SERPs). It measures how effective a search listing is at attracting clicks relative to the number of times it appears (impressions).





